Gateway

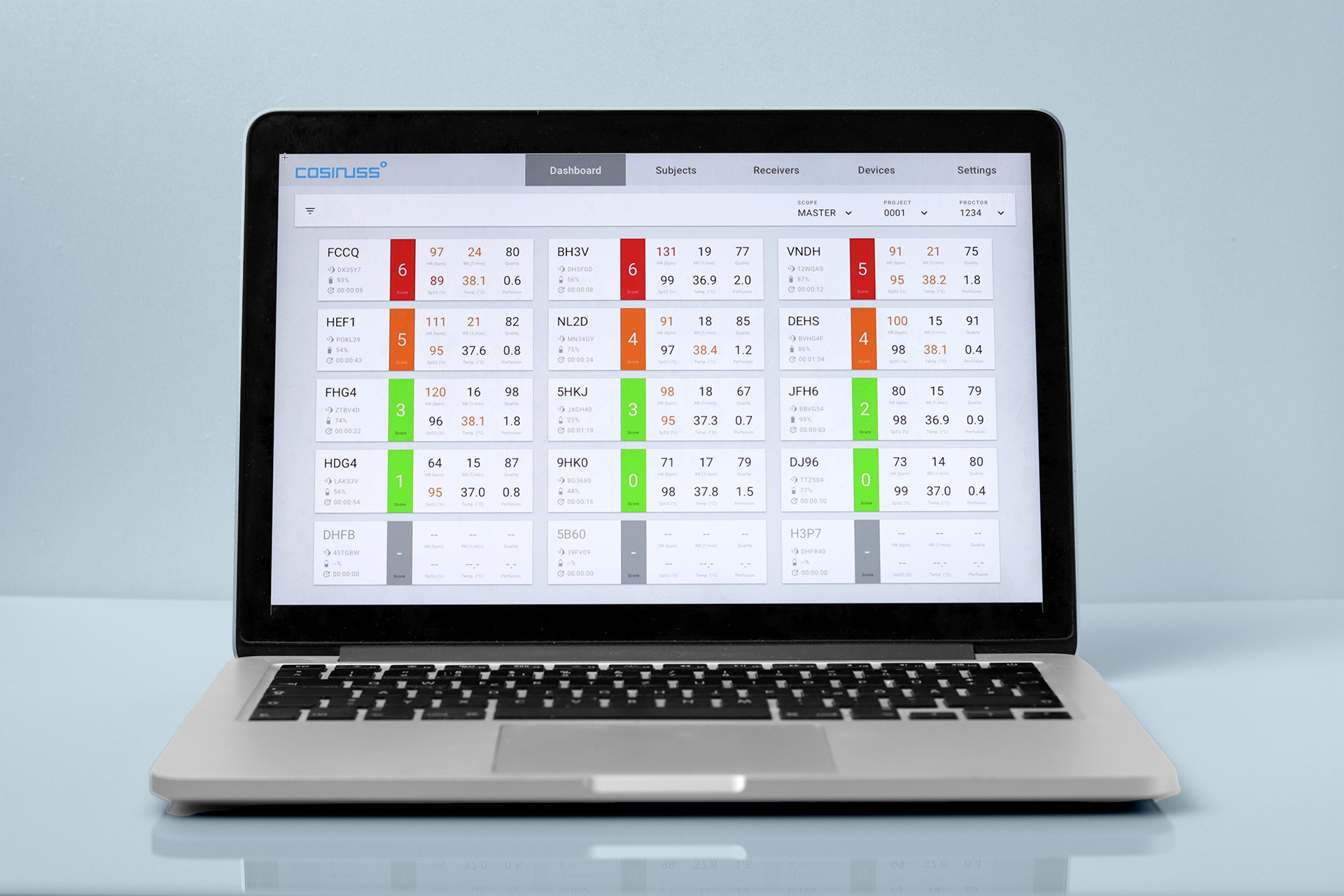
Receiving and forwarding vital signs data with the Gateway
The Gateway is the optimal connection between the person being measured and their healthcare provider. Controlled, stable and reliable.
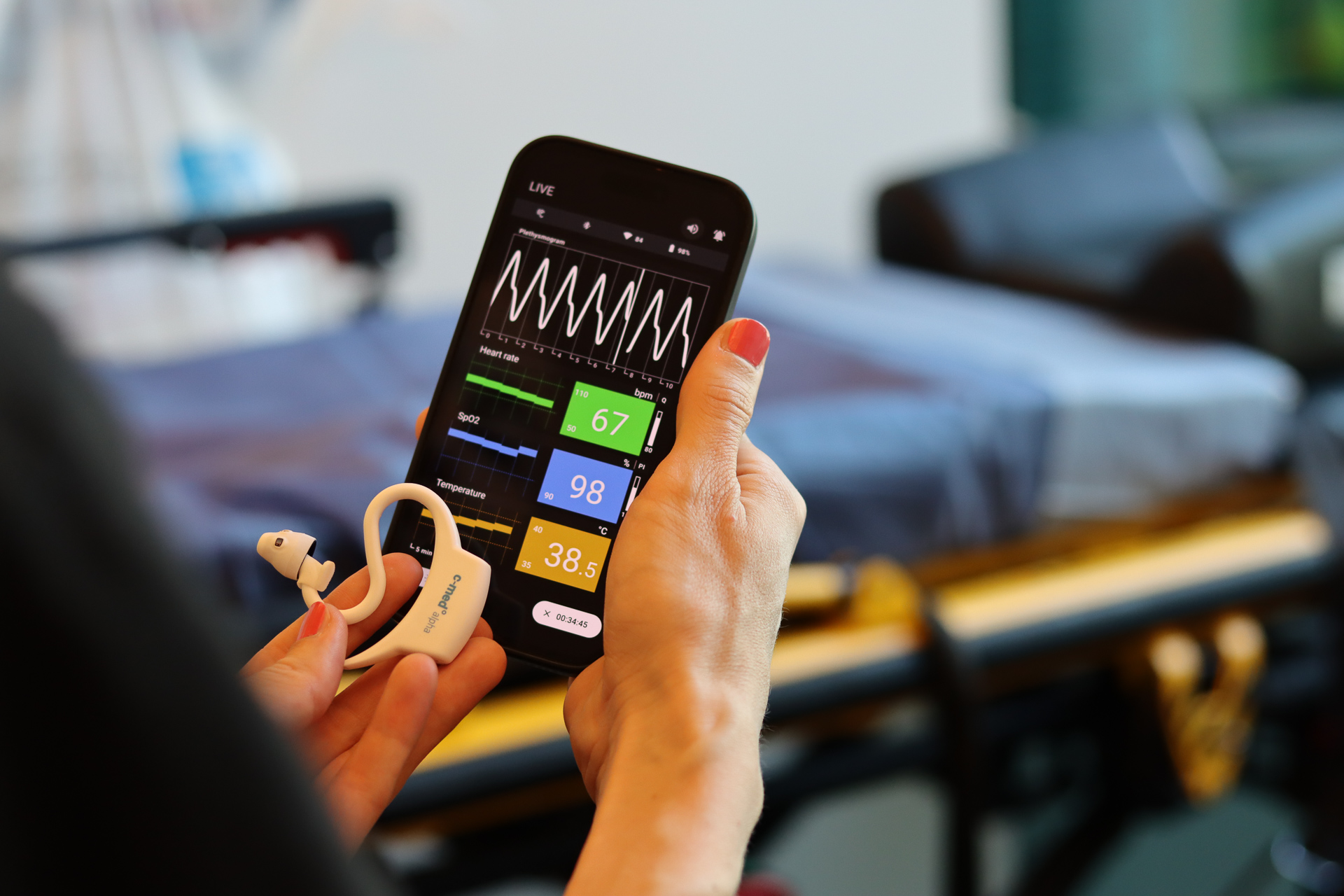
The Gateway is a small microcomputer running with cosinuss° software. This was specially developed for remote monitoring of vital parameters to ensure stable reception and transmission of data. The Gateway receives data from the in-ear sensors via Bluetooth and forwards it to the cosinuss° Health Platform. All data is collected pseudonymously.
Connection between cosinuss° sensors and Gateway
The small Gateway has a Bluetooth interface that can receive vital signs via the standard services as well as the high-resolution PPG and raw acceleration data via the special cosinuss° services. The data is temporarily stored by the Gateway and forwarded when a network connection is active.
Connection between Gateway and cosinuss° Health Platform
The Gateway’s computing capacity enables real-time forwarding to mobile telecommunication networks. There is also the possibility of a wired LAN connection or the integration of the Gateway into an existing WLAN. Optionally, the data can also be transmitted to LTE or even 5G mobile networks using a SIM stick.
For long-term remote monitoring
If a long-term or permanent setup is planned for remote monitoring of persons who are in a fixed environment (e.g. at home), the Gateway offers significant advantages. After the setup of the Gateway or – in case of larger movement radius of the monitored person – of several connected Gateways is completed, the transmission of the measured data takes place reliably and automatically. The measured person can move freely within the Bluetooth range and does not have to think about any manual actions or taking the Gateway with him. This enables extremely low susceptibility to errors and thus high reliability in remote monitoring.
Further advantages of the Gateway
- The Gateway is operated with a wired power connection. Battery charging is therefore not necessary.
- Unlike with an app, there is no need for the collection and storage of mobile phone numbers, location data, user accounts or other smartphone-specific data
- that can be associated with a person’s identity.
- The behavior of the Gateway, such as cyclic measurement intervals, can be configured at any time.
- The Gateway continuously receives new updates.
- Several Gateways can be connected together to form a mesh network.
- The Gateway has several possibilities for network connection.
- If a network connection is not possible, the Gateway has sufficient memory capacity even for longer offline measurements.
- Optionally, the Gateway offers enough computing capacity for additional signal processing or application of algorithms (e.g. calculation of respiratory rate) apart from the cosinuss° Health Platform.
- All activities of the Gateway software are logged and made available transparently, which increases traceability.
- Unlike with apps, the monitoring application is not pushed into the background or even deactivated by the operating system.
- Sleep mode, flight mode or similar device modes that could interfere with Bluetooth reception or data transmission are excluded.
- Unlike with apps, no other data is collected by the operating system and passed on to third parties.
Compatibility
- cosinuss° In-Ear Sensors: cosinuss° One, cosinuss° Two, c-med° alpha
- cosinuss° Health Platform: Yes
- Third-party provider: Yes (see data sheet for details)
Interfaces
- Data input: Bluetooth, custom and standard services
- Data output: LAN, WiFi, mobile networks
Selected references
Telecovid – Remote Patient Monitoring for COVID-19 | University Hospital in Munich / 2020 – 2021
Related research articles:
- Wurzer D, Spielhagen P, Siegmann A, Gercekcioglu A, Gorgass J, et al.: “Remote monitoring of COVID-19 positive high-risk patients in domestic isolation: A feasibility study”. PLOS ONE 16(9), 2021.
- M. Baldinger, et al.,“TELECOVID: Remote Vital Signs Monitoring of COVID-19 Risk Patients in Home Isolation With an In-Ear Wearable“ in IEEE Pervasive Computing, vol. 20, no. 02, pp. 58-62, 2021.
DiAssCo – Full recovery from intensive station to home – COVID-19 | University Hospital LMU in Munich / 2021
Telecovid-Innsbruck | University of Innsbruck (Prof. G. Pölzl)
Epitect | Nursing support for people with epilepsy through innovative ear sensor technology (EPItect) | University Hospital for Epileptology Bonn, Fraunhofer Institute for Software and Systems Engineering ISST, Clinic for Neuropediatrics at Kiel University, North German Epilepsy Center in Schwentinental-Raisdorf, cosinuss° GmbH, München / 03/16 – 02/19
Gait Classification | C. P. Burgos et al., “In-Ear Accelerometer-Based Sensor for Gait Classification,” in IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 20, no. 21, pp. 12895-12902, 1 Nov.1, 2020.
Telemedicine with objective data – RPM | University Hospital in Denmark / 2021
360° data integration – EMERGENCY CARE | University in Sweden / 2021
Energy expenditure | Technical University of Munich (TUM) Faculty of Sport and Health Science (Dr. Martin Schönfelder)